

The Standard English unit is pounds mass per cubic foot ( lbm/ft 3). The standard SI unit is kilograms per cubic meter ( kg/m 3). In other words, the density (ρ) of a substance is the total mass (m) of that substance divided by the total volume (V) occupied by that substance. It is an intensive property, which is mathematically defined as mass divided by volume: Typical densities of various substances at atmospheric pressure.ĭensity is defined as the mass per unit volume. How does the atomic mass determine the density of materials? Density of Lead The atomic mass number determines especially the atomic mass of atoms. The mass number is different for each different isotope of a chemical element. For 63Cu, the atomic mass is less than 63, so this must be the dominant factor. A nucleus with greater binding energy has lower total energy, and therefore a lower mass according to Einstein’s mass-energy equivalence relation E = mc 2. The nuclear binding energy varies between nuclei.This increases the mass of nuclei with more neutrons than protons relative to the atomic mass unit scale based on 12C with equal numbers of protons and neutrons.

The neutron is slightly heavier than the proton.There are two reasons for the difference between mass number and isotopic mass, known as the mass defect: For example, 63Cu (29 protons and 34 neutrons) has a mass number of 63, and an isotopic mass in its nuclear ground state is 62.91367 u. For other isotopes, the isotopic mass usually differs and is usually within 0.1 u of the mass number. One unified atomic mass unit is approximately the mass of one nucleon (either a single proton or neutron) and is numerically equivalent to 1 g/mol.įor 12C, the atomic mass is exactly 12u, since the atomic mass unit is defined from it. One atomic mass unit is equal to 1.66 x 10 -24 grams. The unit of measure for mass is the atomic mass unit (amu).
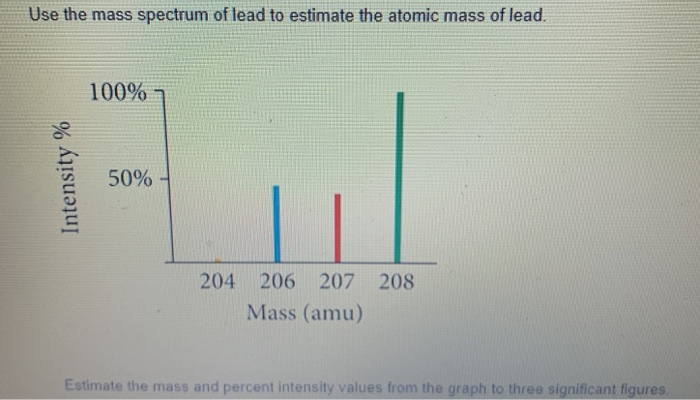
Therefore this resulting atomic mass is calculated from naturally-occurring isotopes and their abundance. The atomic symbol and name of an atom with the same mass number as in part b. Note that each element may contain more isotopes. The atomic symbol of another isotope of lead with 132 neutrons is 214 82 P b. How does the atomic number determine the chemical behavior of atoms? Atomic Mass of Lead Lead Metal Symbol: Pb Atomic number: 82 Atomic mass: 207.2 Group: Metal CAS-number: Physical data Isotopes Other info Go to element Physical data Electronic data Shells: 2, 8, 18, 32, 18, 4 Orbitals: Xe 4f 14 5d 10 6s 2 6p 2 Electronegativity: 1.9, 1.6 1. Since the number of electrons is responsible for the chemical behavior of atoms, the atomic number identifies the various chemical elements. You will need to refer to a periodic table for proton values.Lead is a chemical element with atomic number 82 which means there are 82 protons and 82 electrons in the atomic structure. In this notation, the atomic number is not included. Belonging to the family of post-transition metals, it has 35 isotopes with mass numbers ranging from 181 to 125 of which Pb-206, Pb-207, and Pb-208 have a stable half-life 3, 4. Symbol-mass format for the above atom would be written as Cr-52. For an example of this notation, look to the chromium atom shown below:Īnother way to refer to a specific atom is to write the mass number of the atom after the name, separated by a hyphen. The "A" value is written as a superscript while the "Z" value is written as a subscript. Both the atomic number and mass are written to the left of the chemical symbol. The composition of any atom can be illustrated with a shorthand notation called A/Z format.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
